- mybaits大多数用在spring整合中,这里介绍Spring整合Mybatis的配置
Spring整合Mybatis的配置
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.xxx.entity"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/* .xml"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.xxx.dao"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
先看一下SqlSessionFactoryBean的类图
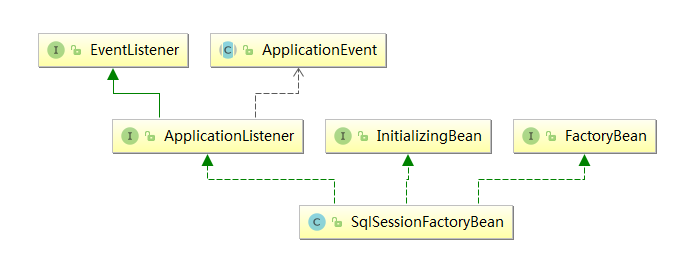 其中,FactoryBean和InitializingBean,我们知道,实现了FactoryBean的bean会调用它的getObject方法创建bean,实现了InitializingBean的bean会在属性填充完成之后调用它的afterPropertiesSet方法,我们就来分析这个方法:
其中,FactoryBean和InitializingBean,我们知道,实现了FactoryBean的bean会调用它的getObject方法创建bean,实现了InitializingBean的bean会在属性填充完成之后调用它的afterPropertiesSet方法,我们就来分析这个方法:
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// 属性校验
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
/* 构建SqlSessionFactory */
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
SqlSessionFactoryBean:
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
// Configuration的几种配置
if (this.configuration != null) {
configuration = this.configuration;
if (configuration.getVariables() == null) {
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
configuration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
}
configuration = new Configuration();
if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
}
}
// objectFactory配置
if (this.objectFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectFactory(this.objectFactory);
}
// objectWrapperFactory配置
if (this.objectWrapperFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectWrapperFactory(this.objectWrapperFactory);
}
// vfs配置
if (this.vfs != null) {
configuration.setVfsImpl(this.vfs);
}
// typeAliasesPackage配置
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
String[] typeAliasPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeAliasesPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeAliasPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(packageToScan,
typeAliasesSuperType == null ? Object.class : typeAliasesSuperType);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for aliases");
}
}
}
// typeAliases配置
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
for (Class<?> typeAlias : this.typeAliases) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
}
}
}
// plugins配置
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
for (Interceptor plugin : this.plugins) {
configuration.addInterceptor(plugin);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
}
}
}
// typeHandlersPackage配置
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
String[] typeHandlersPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeHandlersPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeHandlersPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(packageToScan);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for type handlers");
}
}
}
// typeHandlers配置
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
for (TypeHandler<?> typeHandler : this.typeHandlers) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
}
}
}
// databaseIdProvider配置
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
try {
configuration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
// cache配置
if (this.cache != null) {
configuration.addCache(this.cache);
}
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
// 如果配置了configLocation,则解析配置文件
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
if (this.transactionFactory == null) {
// 如果没有transactionFactory配置,应用SpringManagedTransactionFactory
this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory();
}
// 为Configuration设置环境
configuration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource));
// mapperLocations配置
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
// 解析mapper配置
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
}
// 构建SqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
整个过程就是对Mybatis的各种配置的设置和解析并构建SqlSessionFactory,方法中有一个步骤是如果用户没有配置transactionFactory,默认将Mybatis的transactionFactory配置为SpringManagedTransactionFactory,我们在分析Mybatis源码的时候看到,在用户没有指定transactionFactory配置的时候,Mybatis使用ManagedTransactionFactory作为默认的TransactionFactory,Mybatis在创建SqlSession时,需要为其添加一个Executor执行器,构建Executor执行器时需要的Transaction对象就是通过TransactionFactory的newTransaction方法创建的,后续Executor执行sql命令时会通过Transaction的getConnection方法获取数据库连接,这里添加的SpringManagedTransactionFactory有什么作用呢?我们可以思考一下,Spring在开启事务的时候需要获取数据库连接,Mybatis执行的时候也要获取数据库连接,在一次调用过程中,两者配合使用时,如果想让Spring的事务作用于Mybatis的数据库操作,那么在这次调用的过程中两者肯定要共用同一个数据库连接,不然事务无法生效,SpringManagedTransactionFactory就可以解决共用数据库连接的问题,我们来分析这个过程:
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new SpringManagedTransaction(dataSource);
}
SpringManagedTransactionFactory的newTransaction方法会返回SpringManagedTransaction,所以Executor获取数据库连接时就会调用SpringManagedTransaction的getConnection方法:
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection(); /* 开启数据库连接 */
}
return this.connection;
}
SpringManagedTransaction:
private void openConnection() throws SQLException {
/* 获取数据库连接 */
this.connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.dataSource);
this.autoCommit = this.connection.getAutoCommit();
this.isConnectionTransactional = DataSourceUtils.isConnectionTransactional(this.connection, this.dataSource);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug(
"JDBC Connection ["
+ this.connection
+ "] will"
+ (this.isConnectionTransactional ? " " : " not ")
+ "be managed by Spring");
}
}
DataSourceUtils:
public static Connection getConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws CannotGetJdbcConnectionException {
try {
/* 获取数据库连接 */
return doGetConnection(dataSource);
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new CannotGetJdbcConnectionException("Could not get JDBC Connection", ex);
}
}
DataSourceUtils:
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
// 从当前线程中获取绑定的ConnectionHolder
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
// 如果ConnectionHolder不为null并且持有数据库连接或者与事务同步
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
// 将ConnectionHolder请求数+1
conHolder.requested();
// 如果ConnectionHolder没有持有数据库连接则获取数据库连接放入ConnectionHolder
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource");
conHolder.setConnection(dataSource.getConnection());
}
// 返回数据库连接
return conHolder.getConnection();
}
logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource");
// 当前线程没有ConnectionHolder,获取数据库连接
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
// 判断当前线程的事务同步是否处于活动状态
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
logger.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for JDBC Connection");
// 在事务中使用相同的连接进一步JDBC操作,线程绑定对象将在事务完成时被同步删除
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
if (holderToUse == null) {
// ConnectionHolder为null则创建新的ConnectionHolder
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}
else {
// 不为null则将数据库连接放入ConnectionHolder
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
holderToUse.requested(); // 将ConnectionHolder请求数+1
// 为当前线程注册一个新的事务同步
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
// 将SqlSessionHolder标记为与事务同步
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
// 如果是新的ConnectionHolder,则绑定到当前线程
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}
return con;
}
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
// 从当前线程中获取绑定的ConnectionHolder
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
// 如果ConnectionHolder不为null并且持有数据库连接或者与事务同步
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
// 将ConnectionHolder请求数+1
conHolder.requested();
// 如果ConnectionHolder没有持有数据库连接则获取数据库连接放入ConnectionHolder
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource");
conHolder.setConnection(dataSource.getConnection());
}
// 返回数据库连接
return conHolder.getConnection();
}
logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource");
// 当前线程没有ConnectionHolder,获取数据库连接
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
// 判断当前线程的事务同步是否处于活动状态
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
logger.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for JDBC Connection");
// 在事务中使用相同的连接进一步JDBC操作,线程绑定对象将在事务完成时被同步删除
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
if (holderToUse == null) {
// ConnectionHolder为null则创建新的ConnectionHolder
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}
else {
// 不为null则将数据库连接放入ConnectionHolder
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
holderToUse.requested(); // 将ConnectionHolder请求数+1
// 为当前线程注册一个新的事务同步
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
// 将SqlSessionHolder标记为与事务同步
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
// 如果是新的ConnectionHolder,则绑定到当前线程
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}
return con;
}
这里我们看到通过调用TransactionSynchronizationManager的getResource方法获取当前线程绑定的ConnectionHolder,TransactionSynchronizationManager这个类我们在分析Spring事务源码的时候看到过,用来管理每个线程的资源和事务同步,内部维护了很多ThreadLocal变量来保存一些线程相关的资源。方法中我们发现有一个注册事务同步的过程,这个事务同步是做什么用的呢?我们在分析Spring事务源码的时候提到过,在Spring事务回滚、提交、挂起等操作时会激活事务同步的相关方法,而这里添加的事务同步的作用主要是在Spring事务提交、回滚等操作后将ConnectionHolder的请求数量置为0、将一些属性置为初始状态、将数据库连接放回连接池、释放数据库连接等。
MapperScannerConfigurer的配置
首先看一下类图
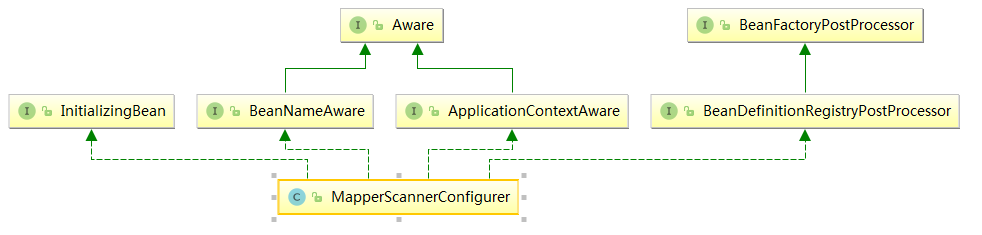
发现它同样实现了InitializingBean,但是它对afterPropertiesSet方法的实现仅仅是校验basePackage属性是否为null。我们来看它实现的另外一个接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,这个接口我们在分析Spring上下文初始化源码的时候介绍过,用于在创建bean之前增加或改变BeanDefinition,我们在介绍它的作用时列举的例子就是MapperScannerConfigurer,我们来看相关方法的实现:
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
/* 处理properties配置 */
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();/* 注册过滤器 */
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
这里为什么要给出处理properties配置的选项呢?properties配置不是由PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer这个bean来完成的么?(如果读者对PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer不熟悉,可以去任何一个使用Spring的工程中去看一下properties的相关配置,不论是直接配置PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer还是使用
MapperScannerConfigurer:
private void processPropertyPlaceHolders() {
Map<String, PropertyResourceConfigurer> prcs = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(PropertyResourceConfigurer.class);
if (!prcs.isEmpty() && applicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
BeanDefinition mapperScannerBean = ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext)
.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(beanName);
// PropertyResourceConfigurer不公开任何显式执行属性占位符替换的方法,代替的是创建一个只包含当前mapper扫描器和后处理工厂的BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
factory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, mapperScannerBean);
for (PropertyResourceConfigurer prc : prcs.values()) {
// 提前执行PropertyResourceConfigurer的postProcessBeanFactory方法加载properties
prc.postProcessBeanFactory(factory);
}
PropertyValues values = mapperScannerBean.getPropertyValues();
// 更新需要替换的属性
this.basePackage = updatePropertyValue("basePackage", values);
this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName = updatePropertyValue("sqlSessionFactoryBeanName", values);
this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName = updatePropertyValue("sqlSessionTemplateBeanName", values);
}
}
ClassPathMapperScanner:
public void registerFilters() {
boolean acceptAllInterfaces = true;
// 如果指定了annotationClass配置,则添加注解类型过滤器,使用给定的注解和/或标记接口
if (this.annotationClass != null) {
addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(this.annotationClass));
acceptAllInterfaces = false;
}
// 如果指定了markerInterface配置,则添加可分配给定类型的过滤器,重写AssignableTypeFilter忽略实际标记接口上的匹配
if (this.markerInterface != null) {
addIncludeFilter(new AssignableTypeFilter(this.markerInterface) {
@Override
protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
return false;
}
});
acceptAllInterfaces = false;
}
// 如果上面两个没有配置,则添加接受所有接口的过滤器
if (acceptAllInterfaces) {
addIncludeFilter(new TypeFilter() {
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
return true;
}
});
}
// 添加过滤掉package-info.java的过滤器
addExcludeFilter(new TypeFilter() {
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
String className = metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName();
return className.endsWith("package-info");
}
});
}
相关属性设置完成之后就可以开始进行文件的扫描了: ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner:
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages); /* 包扫描 */
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
// 注册注解处理器
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
ClassPathMapperScanner:
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
// 调用父类的doScan方法进行扫描
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
/* 处理扫描到的BeanDefinition */
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
扫描的过程其实我们在分析Spring注解扫描的源码的时候已经分析过了,这里的扫描流程同样是复用这个流程,流程中使用的过滤器就是上文中注册的过滤器,这里不再重复这个流程,这里给出文章链接,读者可以去回顾一下这个流程,传送门。下面我们来分析对扫描到的BeanDefinition的处理: ClassPathMapperScanner:
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName()
+ "' and '" + definiti.. on.getBeanClassName() + "' mapperInterface");
}
// mapper的接口是bean的原始类,但是,实际的bean类是MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName());
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass());
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
// 下面是一些其他属性的添加
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
}
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
}
}
}
我们看到这里为扫描到的BeanDefinition设置了BeanClass为MapperFactoryBean,我们来看一下这个类的层次结构:
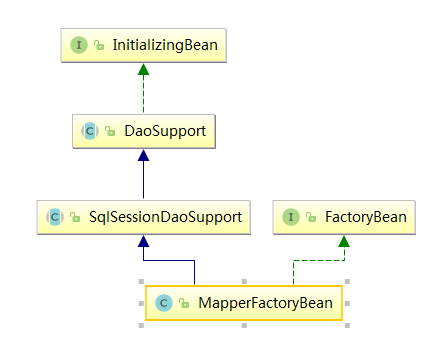 我们发现它同样实现了InitializingBean和FactoryBean,我们分析相关实现方法:
DaoSupport:
我们发现它同样实现了InitializingBean和FactoryBean,我们分析相关实现方法:
DaoSupport:
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
checkDaoConfig(); /* 检查dao配置 */
try {
initDao(); // 子类扩展初始化dao,默认空实现
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}
MapperFactoryBean:
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig(); /* 调用父类方法进行dao配置检查 */
// 检查mapper接口不能为null
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
// 如果Mybatis的Configuration配置中没有当前mapper,则添加
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
SqlSessionDaoSupport:
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
notNull(this.sqlSession, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required");
}
这里判断了sqlSession属性不能为null,我们在上文中分析处理扫描后的BeanDefinition的过程时,并没有看到为mapper的BeanDefinition增加sqlSession属性,那么MapperFactoryBean创建以后这个属性不就是应该为null么?这里的断言不就无法通过了么?我们知道,SqlSession是通过SqlSessionFactory创建的,处理扫描后的BeanDefinition时为其添加了sqlSessionFactory属性,所以我们尝试从sqlSessionFactory的setter方法中寻找答案: SqlSessionDaoSupport:
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (!this.externalSqlSession) {
/* 创建SqlSessionTemplate */
this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
SqlSessionTemplate:
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
/* 调用重载构造方法 */
this(sqlSessionFactory, sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getDefaultExecutorType());
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType) {
/* 调用重载构造方法 */
this(sqlSessionFactory, executorType,
new MyBatisExceptionTranslator(
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(), true));
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
// 创建sqlSession代理
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
我们发现这里创建了一个sqlSession的代理,它有什么用呢?我们知道,我们可以使用SqlSession执行mapper的方法,也可以用它来获取mapper,而SqlSessionTemplate实现了SqlSession并实现了相关方法,方法的功能则委托给了sqlSessionProxy来实现,eg:
SqlSessionTemplate:
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.<T> selectOne(statement, parameter);
}
动态代理的InvocationHandler角色是SqlSessionInterceptor,我们来看它的invoke方法: SqlSessionInterceptor:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/* 获取sqlSession */
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
// 执行sqlSession的对应方法
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
// 如果sqlSession不是由Spring管理的,则提交sqlSession
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// 强制提交sqlSession,因为一些数据库在调用close方法之前需要提交/回滚。
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory); // 关闭SqlSession
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory); // 关闭SqlSession
}
}
}
SqlSessionUtils:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
// 获取当前线程绑定的SqlSessionHolder
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
/* 从SqlSessionHolder中获取SqlSession */
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session; // 当前线程存在则直接返回
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
// 没有通过SqlSessionFactory获取新的SqlSession
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
/* 绑定SessionHolder到当前线程 */
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
private static SqlSession sessionHolder(ExecutorType executorType, SqlSessionHolder holder) {
SqlSession session = null;
// 如果SqlSessionHolder不为null并且与事务同步
if (holder != null && holder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
if (holder.getExecutorType() != executorType) {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException("Cannot change the ExecutorType when there is an existing transaction");
}
// 将SqlSessionHolder请求数+1
holder.requested();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Fetched SqlSession [" + holder.getSqlSession() + "] from current transaction");
}
// 获取SqlSession返回
session = holder.getSqlSession();
}
return session;
}
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
// 判断当前线程的事务同步是否处于活动状态
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
// 上文创建SqlSessionFactory时判断如果没有transactionFactory配置,应用SpringManagedTransactionFactory
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
// 创建SqlSessionHolder持有SqlSession
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
// 绑定到当前线程
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
// 为当前线程注册一个新的事务同步
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
// 将SqlSessionHolder标记为与事务同步
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
// 将SqlSessionHolder请求数+1
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
}
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
}
}
这里添加的事务同步的作用主要是在Spring事务提交回滚等操作后调用SqlSession的commit、close等方法来做关闭和提交等操作。
我们继续来分析MapperFactoryBean对FactoryBean接口getObject方法也就是创建bean的方法的实现:
public T getObject() throws Exception {
/* 获取mapper */
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
这里的getSqlSession方法返回的也就是我们上文分析的SqlSessionTemplate。 SqlSessionTemplate:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
这个方法的内容我们应该很熟悉了,在分析Mybatis源码的时候已经看到过,调用Mybatis的Configuration对象的getMapper方法来获取mapper,不熟悉的同学可以阅读笔者关于Mybatis源码分析的文章,有很详细的说明,同样有mapper执行过程的源码分析。到这里,整个Spring整合Mybatis的源码分析就完成了。