Dubbo的使用很简单,如果要掌握,需要详细分析源码。
SPI机制
SPI全称(service provider interface),是JDK内置的一种服务提供发现机制,目前市面上有很多框架都是用它来做服务的扩展发现,大家耳熟能详的如JDBC、日志框架都有用到;
简单来说,它是一种动态替换发现的机制。举个简单的例子,如果我们定义了一个规范,需要第三方厂商去实现,那么对于我们应用方来说,只需要集成对应厂商的插件,既可以完成对应规范的实现机制。 形成一种插拔式的扩展手段。
代码实例:
定义规范:
public interface DataBaseDriver {
String connect(String hospt);
}
MysqlDriver去实现:
public class MysqlDriver implements DataBaseDriver{
@Override
public String connect(String s) {
return "begin build Mysql connection";
}
}
//并且在resources/services/com.XX.spi.DataBaseDriver文件中添加
//com.gupaoedu.spi.MysqlDriver
测试demo:
public class DataBaseConnection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServiceLoader<DataBaseDriver> serviceLoader=
ServiceLoader.load(DataBaseDriver.class);
for(DataBaseDriver driver:serviceLoader){
System.out.println(driver.connect("localhost"));
}
}
}
//将实现者的项目添加到测试pom中
SPI的缺点
1 JDK标准的SPI会一次性加载实例化扩展点的所有实现,什么意思呢?就是如果你在META-INF/service下的文件里面加了N个实现类,那么JDK启动的时候都会一次性全部加载。那么如果有的扩展点实现初始化很耗时或者如果有些实现类并没有用到,那么会很浪费资源
2 如果扩展点加载失败,会导致调用方报错,而且这个错误很难定位到是这个原因
Dubbo优化后的SPI实现
Dubbo的SPI机制规范
大部分的思想都是和SPI是一样,只是下面两个地方有差异。
1 需要在resource目录下配置META-INF/dubbo或者META-INF/dubbo/internal或者META-INF/services,并基于SPI接口去创建一个文件
2 文件名称和接口名称保持一致,文件内容和SPI有差异,内容是KEY对应Value
跟源码查看详细的过程
SPI接口定义
定义了@SPI注解
public @interface SPI {
Stringvalue() default ""; //指定默认的扩展点
}
只有在接口打了@SPI注解的接口类才会去查找扩展点实现
会依次从这几个文件中读取扩展点
META-INF/dubbo/internal/ //dubbo内部实现的各种扩展都放在了这个目录了
META-INF/dubbo/
META-INF/services/
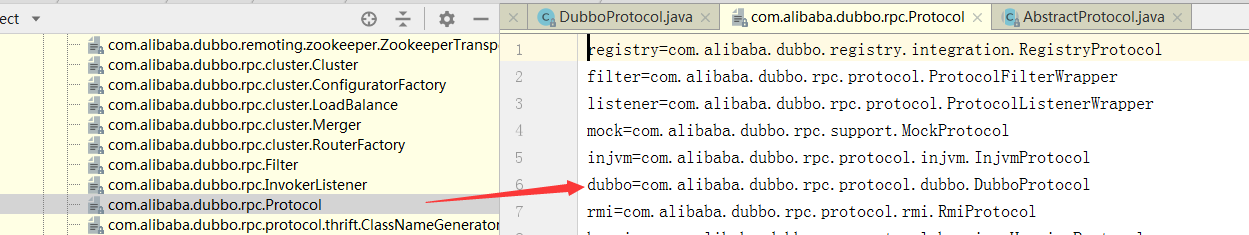
我们以Protocol接口为例, 接口上打上SPI注解,默认扩展点名字为dubbo
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface Protocol {
int getDefaultPort();
@Adaptive
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> var1) throws RpcException;
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> var1, URL var2) throws RpcException;
void destroy();
}
看看该接口的类图
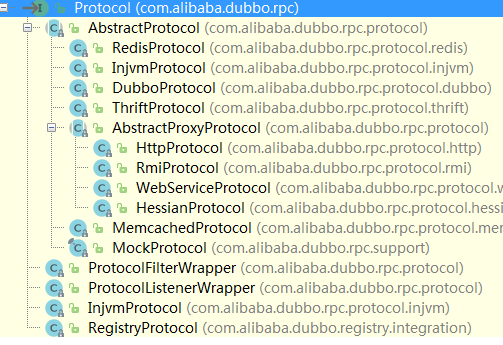
了解了基本设计之后开始研究使用
测试demo
//研究一下下边代码的实现过程,输出dubbo
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getDefaultExtensionName();
跟源码:ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class)
//Type为Protocol
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(Class<T> type) {
if (type == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null");
if(!type.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type + ") is not interface!");
}
if(!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type +
") is not extension, because WITHOUT @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + " Annotation!");
}
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) {
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));
loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
return loader;
}
跟源码:new ExtensionLoader
private ExtensionLoader(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension());
//此处由于是protocol
//则先ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class),此举又会调用,再次调入该函数时
//type=ExtensionFactory
//objectFactory=null
//返回的loader为ExtensionLoader<ExtensionFactory>
//继续调用ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension()
}
调用ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension()
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {//多线程的安全机制
if(createAdaptiveInstanceError == null) {
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {//多线程的安全机制
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
//调用ExtensionFactory的createAdaptiveExtension
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(), createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
//继续
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can not create adaptive extenstion " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
//again getAdaptiveExtensionClass
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
getExtensionClasses();
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}
//getExtensionClasses()
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
// loadExtensionClasses()
// 此方法已经getExtensionClasses方法同步过。ExtensionFactory
// @SPI
// public interface ExtensionFactory {
// <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name);
//}
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if(defaultAnnotation != null) { //如上此处为空
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();
if(value != null && (value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if(names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
if(names.length == 1) cachedDefaultName = names[0];
}
}
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY);
return extensionClasses;//得到spiExtensionFactory springExtensionFactory
}
private void loadFile(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, String dir) {
String fileName = dir + type.getName();
try {
Enumeration<java.net.URL> urls;
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
if (urls != null) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
java.net.URL url = urls.nextElement();
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream(), "utf-8"));
try {
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
final int ci = line.indexOf('#');
if (ci >= 0) line = line.substring(0, ci);
line = line.trim();
if (line.length() > 0) {
try {
String name = null;
int i = line.indexOf('=');
if (i > 0) {
name = line.substring(0, i).trim();
line = line.substring(i + 1).trim();
}
if (line.length() > 0) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(line, true, classLoader);
if (! type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class "
+ clazz.getName() + "is not subtype of interface.");
}
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
if(cachedAdaptiveClass == null) {
cachedAdaptiveClass = clazz;//这里讲AdaptiveExtensionFactory存储到cachedAdaptiveClass
} else if (! cachedAdaptiveClass.equals(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("More than 1 adaptive class found: "
+ cachedAdaptiveClass.getClass().getName()
+ ", " + clazz.getClass().getName());
}
} else {
try {
clazz.getConstructor(type);
Set<Class<?>> wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (wrappers == null) {
cachedWrapperClasses = new ConcurrentHashSet<Class<?>>();
wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
}
wrappers.add(clazz);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
clazz.getConstructor();
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
name = findAnnotationName(clazz);
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
if (clazz.getSimpleName().length() > type.getSimpleName().length()
&& clazz.getSimpleName().endsWith(type.getSimpleName())) {
name = clazz.getSimpleName().substring(0, clazz.getSimpleName().length() - type.getSimpleName().length()).toLowerCase();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + url);
}
}
}
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name);
if (names != null && names.length > 0) {
Activate activate = clazz.getAnnotation(Activate.class);
if (activate != null) {
cachedActivates.put(names[0], activate);
}
for (String n : names) {
if (! cachedNames.containsKey(clazz)) {
cachedNames.put(clazz, n);
}
Class<?> c = extensionClasses.get(n);
if (c == null) {
extensionClasses.put(n, clazz);
} else if (c != clazz) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate extension " + type.getName() + " name " + n + " on " + c.getName() + " and " + clazz.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("Failed to load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class line: " + line + ") in " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
exceptions.put(line, e);
}
}
} // end of while read lines
} finally {
reader.close();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class file: " + url + ") in " + url, t);
}
} // end of while urls
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", description file: " + fileName + ").", t);
}
}
@Adaptive
public class AdaptiveExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
private final List<ExtensionFactory> factories;
public AdaptiveExtensionFactory() {
ExtensionLoader<ExtensionFactory> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class);
List<ExtensionFactory> list = new ArrayList<ExtensionFactory>();
for (String name : loader.getSupportedExtensions()) {
list.add(loader.getExtension(name));
}
factories = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);//此处实例花了得到spiExtensionFactory springExtensionFactory
}
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
for (ExtensionFactory factory : factories) {
T extension = factory.getExtension(type, name);
if (extension != null) {
return extension;
}
}
return null;
}
}
//将AdaptiveExtensionFactory实例化后
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
try {
if (objectFactory != null) {//objectFactory为空
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
if (method.getName().startsWith("set")
&& method.getParameterTypes().length == 1
&& Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
try {
String property = method.getName().length() > 3 ? method.getName().substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + method.getName().substring(4) : "";
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property);
if (object != null) {
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("fail to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;//实例化的AdaptiveExtensionFactory
}
接着返回到objectFactory
private ExtensionLoader(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension());//实例化的AdaptiveExtensionFactory
}
获取默认名字
public String getDefaultExtensionName() {
getExtensionClasses();
return cachedDefaultName;
}
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
//又继续操作// 此方法已经getExtensionClasses方法同步过。
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if(defaultAnnotation != null) {
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();//value="dubbo"
if(value != null && (value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if(names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
if(names.length == 1) cachedDefaultName = names[0];//cachedDefaultName为dubbo
}
}
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY);
return extensionClasses;
}
如果调用ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension()
由于Protocol的子类没有被@Adaptive注解的类,所以如下:
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
getExtensionClasses();
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();//将生产adaptive
}
//again
private Class<?> createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
String code = createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode();
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();//当前类的ClassLoader
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
//@Adaptive
//public class AdaptiveCompiler implements Compiler {},获取了一个AdaptiveCompiler的实例
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
public Class<?> compile(String code, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Compiler compiler;
ExtensionLoader<Compiler> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Compiler.class);
String name = DEFAULT_COMPILER; // copy reference
if (name != null && name.length() > 0) {
compiler = loader.getExtension(name);
} else {
compiler = loader.getDefaultExtension();
//@SPI("javassist")
//public interface Compiler {}获取默认的javassistcompile
}
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);//生产代理类
}
生产代码的逻辑:(完全没有Adaptive方法,则不需要生成Adaptive类)
private String createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode() {
StringBuilder codeBuidler = new StringBuilder();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
boolean hasAdaptiveAnnotation = false;
for(Method m : methods) {
if(m.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
hasAdaptiveAnnotation = true;
break;
}
}
// 完全没有Adaptive方法,则不需要生成Adaptive类
if(! hasAdaptiveAnnotation)
throw new IllegalStateException("No adaptive method on extension " + type.getName() + ", refuse to create the adaptive class!");
codeBuidler.append("package " + type.getPackage().getName() + ";");
codeBuidler.append("\nimport " + ExtensionLoader.class.getName() + ";");
codeBuidler.append("\npublic class " + type.getSimpleName() + "$Adpative" + " implements " + type.getCanonicalName() + " {");
for (Method method : methods) {
Class<?> rt = method.getReturnType();
Class<?>[] pts = method.getParameterTypes();
Class<?>[] ets = method.getExceptionTypes();
Adaptive adaptiveAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Adaptive.class);
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder(512);
if (adaptiveAnnotation == null) {
code.append("throw new UnsupportedOperationException(\"method ")
.append(method.toString()).append(" of interface ")
.append(type.getName()).append(" is not adaptive method!\");");
} else {
int urlTypeIndex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; ++i) {
if (pts[i].equals(URL.class)) {
urlTypeIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// 有类型为URL的参数
if (urlTypeIndex != -1) {
// Null Point check
String s = String.format("\nif (arg%d == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"url == null\");",
urlTypeIndex);
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\n%s url = arg%d;", URL.class.getName(), urlTypeIndex);
code.append(s);
}
// 参数没有URL类型
else {
String attribMethod = null;
// 找到参数的URL属性
LBL_PTS:
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; ++i) {
Method[] ms = pts[i].getMethods();
for (Method m : ms) {
String name = m.getName();
if ((name.startsWith("get") || name.length() > 3)
&& Modifier.isPublic(m.getModifiers())
&& !Modifier.isStatic(m.getModifiers())
&& m.getParameterTypes().length == 0
&& m.getReturnType() == URL.class) {
urlTypeIndex = i;
attribMethod = name;
break LBL_PTS;
}
}
}
if(attribMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adative class for interface " + type.getName()
+ ": not found url parameter or url attribute in parameters of method " + method.getName());
}
// Null point check
String s = String.format("\nif (arg%d == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"%s argument == null\");",
urlTypeIndex, pts[urlTypeIndex].getName());
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\nif (arg%d.%s() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"%s argument %s() == null\");",
urlTypeIndex, attribMethod, pts[urlTypeIndex].getName(), attribMethod);
code.append(s);
s = String.format("%s url = arg%d.%s();",URL.class.getName(), urlTypeIndex, attribMethod);
code.append(s);
}
String[] value = adaptiveAnnotation.value();
// 没有设置Key,则使用“扩展点接口名的点分隔 作为Key
if(value.length == 0) {
char[] charArray = type.getSimpleName().toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(128);
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
if(Character.isUpperCase(charArray[i])) {
if(i != 0) {
sb.append(".");
}
sb.append(Character.toLowerCase(charArray[i]));
}
else {
sb.append(charArray[i]);
}
}
value = new String[] {sb.toString()};
}
boolean hasInvocation = false;
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; ++i) {
if (pts[i].getName().equals("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation")) {
// Null Point check
String s = String.format("\nif (arg%d == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"invocation == null\");", i);
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\nString methodName = arg%d.getMethodName();", i);
code.append(s);
hasInvocation = true;
break;
}
}
String defaultExtName = cachedDefaultName;
String getNameCode = null;
for (int i = value.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if(i == value.length - 1) {
if(null != defaultExtName) {
if(!"protocol".equals(value[i]))
if (hasInvocation)
getNameCode = String.format("url.getMethodParameter(methodName, \"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getParameter(\"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("( url.getProtocol() == null ? \"%s\" : url.getProtocol() )", defaultExtName);
}
else {
if(!"protocol".equals(value[i]))
if (hasInvocation)
getNameCode = String.format("url.getMethodParameter(methodName, \"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getParameter(\"%s\")", value[i]);
else
getNameCode = "url.getProtocol()";
}
}
else {
if(!"protocol".equals(value[i]))
if (hasInvocation)
getNameCode = String.format("url.getMethodParameter(methodName, \"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getParameter(\"%s\", %s)", value[i], getNameCode);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getProtocol() == null ? (%s) : url.getProtocol()", getNameCode);
}
}
code.append("\nString extName = ").append(getNameCode).append(";");
// check extName == null?
String s = String.format("\nif(extName == null) " +
"throw new IllegalStateException(\"Fail to get extension(%s) name from url(\" + url.toString() + \") use keys(%s)\");",
type.getName(), Arrays.toString(value));
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\n%s extension = (%<s)%s.getExtensionLoader(%s.class).getExtension(extName);",
type.getName(), ExtensionLoader.class.getSimpleName(), type.getName());
code.append(s);
// return statement
if (!rt.equals(void.class)) {
code.append("\nreturn ");
}
s = String.format("extension.%s(", method.getName());
code.append(s);
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; i++) {
if (i != 0)
code.append(", ");
code.append("arg").append(i);
}
code.append(");");
}
codeBuidler.append("\npublic " + rt.getCanonicalName() + " " + method.getName() + "(");
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; i ++) {
if (i > 0) {
codeBuidler.append(", ");
}
codeBuidler.append(pts[i].getCanonicalName());
codeBuidler.append(" ");
codeBuidler.append("arg" + i);
}
codeBuidler.append(")");
if (ets.length > 0) {
codeBuidler.append(" throws ");
for (int i = 0; i < ets.length; i ++) {
if (i > 0) {
codeBuidler.append(", ");
}
codeBuidler.append(pts[i].getCanonicalName());
}
}
codeBuidler.append(" {");
codeBuidler.append(code.toString());
codeBuidler.append("\n}");
}
codeBuidler.append("\n}");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(codeBuidler.toString());
}
return codeBuidler.toString();
}
因为有adaptive标注的方法生成代码:
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
public class Protocol$Adpative implements com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol {
public void destroy() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("method public abstract void com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.destroy() of
interface com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public int getDefaultPort() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("method public abstract int com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interface com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws java.lang.Class {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Exporter export(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.export(arg0);
}
}
生产了 Protocol$Adpative 实例后由于该Protocol类的extensionfactory
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface Protocol {
/**
* 获取缺省端口,当用户没有配置端口时使用。
*
* @return 缺省端口
*/
int getDefaultPort();
/**
* 暴露远程服务:<br>
* 1. 协议在接收请求时,应记录请求来源方地址信息:RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress();<br>
* 2. export()必须是幂等的,也就是暴露同一个URL的Invoker两次,和暴露一次没有区别。<br>
* 3. export()传入的Invoker由框架实现并传入,协议不需要关心。<br>
*
* @param <T> 服务的类型
* @param invoker 服务的执行体
* @return exporter 暴露服务的引用,用于取消暴露
* @throws RpcException 当暴露服务出错时抛出,比如端口已占用
*/
@Adaptive
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
/**
* 引用远程服务:<br>
* 1. 当用户调用refer()所返回的Invoker对象的invoke()方法时,协议需相应执行同URL远端export()传入的Invoker对象的invoke()方法。<br>
* 2. refer()返回的Invoker由协议实现,协议通常需要在此Invoker中发送远程请求。<br>
* 3. 当url中有设置check=false时,连接失败不能抛出异常,并内部自动恢复。<br>
*
* @param <T> 服务的类型
* @param type 服务的类型
* @param url 远程服务的URL地址
* @return invoker 服务的本地代理
* @throws RpcException 当连接服务提供方失败时抛出
*/
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
/**
* 释放协议:<br>
* 1. 取消该协议所有已经暴露和引用的服务。<br>
* 2. 释放协议所占用的所有资源,比如连接和端口。<br>
* 3. 协议在释放后,依然能暴露和引用新的服务。<br>
*/
void destroy();
}
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
try {
if (objectFactory != null) {//由于此时的objectFactory为AdaptiveExtensionFasctory
//方法没有以set开始的所以不执行
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
if (method.getName().startsWith("set")
&& method.getParameterTypes().length == 1
&& Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
try {
String property = method.getName().length() > 3 ? method.getName().substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + method.getName().substring(4) : "";
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property);
if (object != null) {
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("fail to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;
}
当测试:
System.out.printf(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension().getDefaultPort()+"");
//抛出异常
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: method public ////abstract int com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interface //com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!
分析后总结:
当类上打上SPI标签的时候,可以使用ExtensionLoader进行实例化操作
@SPI 如果有值的话,为默认实现方法如,protocol.class Complie.classes
判断类实现(如:DubboProtocol)上有没有打上@Adaptive注解,如果打上了注解,将此类作为Protocol协议的设配类缓存起来,读取下一行;否则适配类通过javasisit修改字节码生成,关于设配类功能作用后续介绍
如果类没有打上@Adaptive, 判断实现类是否存在入参为接口的构造器(就是DubbboProtocol类是否还有入参为Protocol的构造器),有的话作为包装类缓存到此ExtensionLoader的Set<Class<?»集合中,这个其实是个装饰模式如 ProtocolFilterWrapper
public class ProtocolFilterWrapper implements Protocol {
private final Protocol protocol;
public ProtocolFilterWrapper(Protocol protocol){
if (protocol == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("protocol == null");
}
this.protocol = protocol;
}
如果即不是设配对象也不是wrapped的对象,那就是扩展点的具体实现对象
找实现类上有没有打上@Activate注解,有缓存到变量cachedActivates的map中
将实现类缓存到cachedClasses中,以便于使用时获取
获取或者创建设配对象getAdaptiveExtension
a)如果cachedAdaptiveClass有值,说明有且仅有一个实现类打了@Adaptive, 实例化这个对象返回
b) 如果cachedAdaptiveClass为空, 创建设配类字节码。
为什么要创建设配类,一个接口多种实现,SPI机制也是如此,这是策略模式,但是我们在代码执行过程中选择哪种具体的策略呢。Dubbo采用统一数据模式com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL(它是dubbo定义的数据模型不是jdk的类),它会穿插于系统的整个执行过程,URL中定义的协议类型字段protocol,会根据具体业务设置不同的协议。url.getProtocol()值可以是dubbo也是可以webservice, 可以是zookeeper也可以是redis。
设配类的作用是根据url.getProtocol()的值extName,去ExtensionLoader. getExtension( extName)选取具体的扩展点实现。
所以能够利用javasist生成设配类的条件
1)接口方法中必须至少有一个方法打上了@Adaptive注解
2)打上了@Adaptive注解的方法参数必须有URL类型参数或者有参数中存在getURL()方法
下面给出createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode()方法生成javasist用来生成Protocol适配类后的代码
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension;
public class Protocol$Adpative implements com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol {
//没有打上@Adaptive的方法如果被调到抛异常
public void destroy() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"methodpublic abstract void com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.destroy() of interfacecom.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!")
}
//没有打上@Adaptive的方法如果被调到抛异常
public int getDefaultPort() {
throw newUnsupportedOperationException(
"method public abstractint com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interfacecom.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
//接口中export方法打上@Adaptive注册
publiccom.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Exporter export(
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invokerarg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker{
if (arg0 == null)
throw newIllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invokerargument == null");
//参数类中要有URL属性
if(arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw newIllegalArgumentException( "com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invokerargument getUrl() == null");
//从入参获取统一数据模型URL
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName =(url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
//从统一数据模型URL获取协议,协议名就是spi扩展点实现类的key
if (extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException( "Fail to getextension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") usekeys([protocol])");
//利用dubbo服务查找机制根据名称找到具体的扩展点实现
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension =(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
//调具体扩展点的方法
return extension.export(arg0);
}
//接口中refer方法打上@Adaptive注册
publiccom.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0,
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URLarg1) throws java.lang.Class {
//统一数据模型URL不能为空
if (arg1 == null)
throw newIllegalArgumentException("url == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url =arg1;
//从统一数据模型URL获取协议,协议名就是spi扩展点实现类的key
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ?"dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
if (extName == null)
thrownewIllegalStateException("Failtogetextension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)name from url("+ url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
//利用dubbo服务查找机制根据名称找到具体的扩展点实现
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension =(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class)
.getExtension(extName);
//调具体扩展点的方法
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
}
自动Wrap上扩展点的Wrap类
这是一种装饰模式的实现,在jdk的输入输出流实现中有很多这种设计,在于增强扩展点功能。这里我们拿对于Protocol接口的扩展点实现作为实例讲解。
Dubbo是如何自动的给扩展点wrap上装饰对象的呢?
1)在ExtensionLoader.loadFile加载扩展点配置文件的时候
对扩展点类有接口类型为参数的构造器就是包转对象,缓存到集合中去
2)在调ExtensionLoader的createExtension(name)根据扩展点key创建扩展的时候, 先实例化扩展点的实现, 在判断时候有此扩展时候有包装类缓存,有的话利用包转器增强这个扩展点实现的功能。如下图是实现流程
private T createExtension(String name) {
Class<?> clazz = getExtensionClasses().get(name);
if (clazz == null) {
throw findException(name);
}
try {
T instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
if (instance == null) {
EXTENSION_INSTANCES.putIfAbsent(clazz, (T) clazz.newInstance());
instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
}
injectExtension(instance);
Set<Class<?>> wrapperClasses = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (wrapperClasses != null && wrapperClasses.size() > 0) {
for (Class<?> wrapperClass : wrapperClasses) {
instance = injectExtension((T) wrapperClass.getConstructor(type).newInstance(instance));//这里对protocol进行了包装
}
}
return instance;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Extension instance(name: " + name + ", class: " +
type + ") could not be instantiated: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
IOC大家所熟知的ioc是spring的三大基础功能之一, dubbo的ExtensionLoader在加载扩展实现的时候内部实现了个简单的ioc机制来实现对扩展实现所依赖的参数的注入,dubbo对扩展实现中公有的set方法且入参个数为一个的方法,尝试从对象工厂ObjectFactory获取值注入到扩展点实现中去。
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
try {
if (objectFactory != null) {
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
if (method.getName().startsWith("set")
&& method.getParameterTypes().length == 1
&& Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
try {
String property = method.getName().length() > 3 ? method.getName().substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + method.getName().substring(4) : "";
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property);//看看ObjectFactory是如何根据类型和名字来获取对象的,ObjectFactory也是基于dubbo的spi扩展机制的
if (object != null) {
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("fail to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;
}
看看ObjectFactory是如何根据类型和名字来获取对象的,ObjectFactory也是基于dubbo的spi扩展机制的
它跟Compiler接口一样设配类注解@Adaptive是打在类AdaptiveExtensionFactory上的不是通过javassist编译生成的。
AdaptiveExtensionFactory持有所有ExtensionFactory对象的集合,dubbo内部默认实现的对象工厂是SpiExtensionFactory和SpringExtensionFactory,他们经过TreeMap排好序的查找顺序是优先先从SpiExtensionFactory获取,如果返回空在从SpringExtensionFactory获取。
1) SpiExtensionFactory工厂获取要被注入的对象,就是要获取dubbo spi扩展的实现,所以传入的参数类型必须是接口类型并且接口上打上了@SPI注解,返回的是一个设配类对象。
public class SpiExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
if (type.isInterface() && type.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class)) {
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(type);
if (loader.getSupportedExtensions().size() > 0) {
return loader.getAdaptiveExtension();
}
}
return null;
}
}
2) SpringExtensionFactory,Dubbo利用spring的扩展机制跟spring做了很好的融合。在发布或者去引用一个服务的时候,会把spring的容器添加到SpringExtensionFactory工厂集合中去, 当SpiExtensionFactory没有获取到对象的时候会遍历SpringExtensionFactory中的spring容器来获取要注入的对象
public class SpringExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
private static final Set<ApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashSet<ApplicationContext>();
public static void addApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
contexts.add(context);
}
public static void removeApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
contexts.remove(context);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
for (ApplicationContext context : contexts) {
if (context.containsBean(name)) {
Object bean = context.getBean(name);
if (type.isInstance(bean)) {
return (T) bean;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}