Dubbo使用api与sping两种方式发布服务,以及服务消费。
DUBBo使用Sping发布服务
继承Sping的方式:
1 写一个xml约束文件xsd文件:dubbo使用了dubbo.xsd文件
2 在resources/META-INF/文件夹下写sping.schemas文件
http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/dubbo.xsd
3 在resources/META-INF/文件夹下写sping.handlers文件
http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
4 当sping加载xml时就会按照定义的DubboNamespaceHandler加载文件
?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
</beans>
将每个标签解析成相应的类:
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));//这里实例化了服务发布者对象
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));//这里实例化消费者发布对象
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(AnnotationBean.class, true));
}
}
注意:dubbo是基于sping配置来实现发布服务的,那么一定是基于spring的扩展来写了一套自己的标签,为了在spring启动的时候,也相应的启动provider发布服务注册服务的过程,而同时为了让客户端在启动的时候自动订阅发现服务,加入了两个bean,ServiceBean、ReferenceBean。分别继承了ServiceConfig和ReferenceConfig
同时还分别实现了InitializingBean、DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener, BeanNameAware
InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法。
DisposableBean bean被销毁的时候,spring容器会自动执行destory方法,比如释放资源
pplicationContextAware 实现了这个接口的bean,当spring容器初始化的时候,会自动的将ApplicationContext注入进来
ApplicationListener ApplicationEvent事件监听,spring容器启动后会发一个事件通知
BeanNameAware 获得自身初始化时,本身的bean的id属性
设置了延迟暴露,dubbo在Spring实例化bean(initializeBean)的时候会对实现了InitializingBean的类进行回调,回调方法是afterPropertySet(),如果设置了延迟暴露,dubbo在这个方法中进行服务的发布。
没有设置延迟或者延迟为-1,dubbo会在Spring实例化完bean之后,在刷新容器最后一步发布ContextRefreshEvent事件的时候,通知实现了ApplicationListener的类进行回调onApplicationEvent,dubbo会在这个方法中发布服务。
5 加载完xml文件后,猜想ServiceBean实现了ApplicationListener所以使用onApplicationEvent发布服务
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E var1);
}
6 接下来就着重分析ServiceBean的onApplicationEvent方法:
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (ContextRefreshedEvent.class.getName().equals(event.getClass().getName()) && this.isDelay() && !this.isExported() && !this.isUnexported()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("The service ready on spring started. service: " + this.getInterface());
}
this.export();
}
}
//如果有休眠则休眠,继续调用doexport
if (this.export == null || this.export) {
if (this.delay != null && this.delay > 0) {
delayExportExecutor.schedule(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
ServiceConfig.this.doExport();
}
}, (long)this.delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
this.doExport();
}
}
7 ServiceConfig是ServiceBean的父类,调用父类的synchronized void export() 由于是synchronized则它是原子的发布:
初始化流程的性能调优优先级应该放的比较低,但是安全的优先级应该放的比较高!
经过重重检查之后调用发布逻辑
private void doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, List<URL> registryURLs) {
if (!"none".toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
if (!"remote".toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
this.exportLocal(url);
}
if (!"local".toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Export dubbo service " + this.interfaceClass.getName() + " to url " + url);
}
if (registryURLs != null && registryURLs.size() > 0 && url.getParameter("register", true)) {
Iterator i$ = registryURLs.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
URL registryURL = (URL)i$.next();
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent("dynamic", registryURL.getParameter("dynamic"));
URL monitorUrl = this.loadMonitor(registryURL);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
url = url.addParameterAndEncoded("monitor", monitorUrl.toFullString());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Register dubbo service " + this.interfaceClass.getName() + " url " + url + " to registry " + registryURL);
}
Invoker<?> invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(this.ref, this.interfaceClass, registryURL.addParameterAndEncoded("export", url.toFullString()));
Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export(invoker);
this.exporters.add(exporter);
}
} else {
Invoker<?> invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(this.ref, this.interfaceClass, url);////通过proxyFactory来获取Invoker对象
Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export(invoker);////注册服务
this.exporters.add(exporter);
}
}
}
this.urls.add(url);
}
这个地方可以做一个小结
1 Invoker - 执行具体的远程调用(这块后续单独讲)
2 Protocol – 服务地址的发布和订阅
3 Exporter – 暴露服务或取消暴露
接下来分析proxyFactory.getInvoker(this.ref, this.interfaceClass, url)获取Invoker对象:
// private static final ProxyFactory proxyFactory = (ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ProxyFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
//由于是ProxyFactory的适配器扩展,可以从方法上加载了 @Adaptive({"proxy"}),得知返回了一个适配器类 Protocol$Adaptive
//根据传入的extName得到据地的代理工厂,猜想使用了javassist的ProxyFactory,返回invoker
@SPI("javassist")
public interface ProxyFactory {
@Adaptive({"proxy"})
<T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> var1) throws RpcException;
@Adaptive({"proxy"})
<T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T var1, Class<T> var2, URL var3) throws RpcException;
}
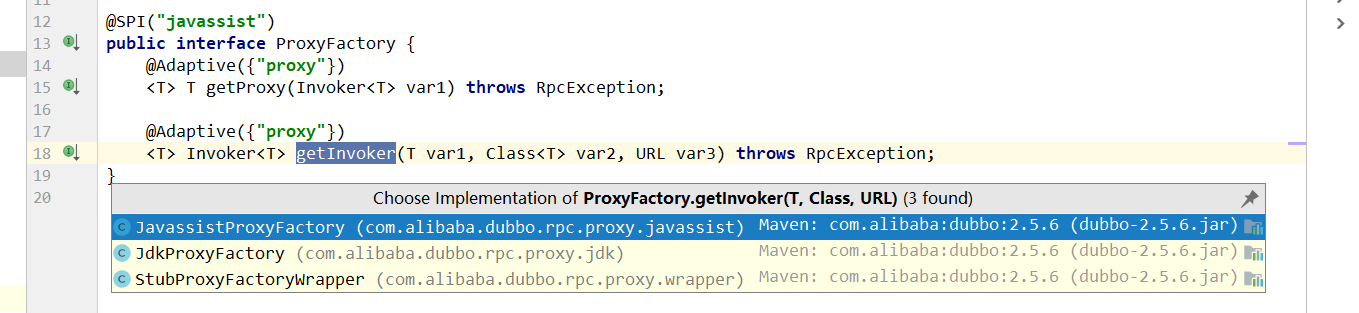
猜想应该是subwraper:
public class StubProxyFactoryWrapper implements ProxyFactory {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StubProxyFactoryWrapper.class);
private final ProxyFactory proxyFactory;
private Protocol protocol;
//由于含有ProxyFactory的构造器,所以肯定了走StubProxyFactoryWrapper
public StubProxyFactoryWrapper(ProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
this.proxyFactory = proxyFactory;
}
//这里使用了注入ioc
public void setProtocol(Protocol protocol) {
this.protocol = protocol;
}
//由于还是调用了this.proxyFactory,因此还是调用javassist的ProxyFactory,其实没有包装
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
return this.proxyFactory.getInvoker(proxy, type, url);
}
}
由于这里调用了getInvoker
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
public JavassistProxyFactory() {
}
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf(36) < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
}
Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf(36) < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type)看看这句话的逻辑:
public static Wrapper getWrapper(Class<?> c) {
while( ClassGenerator.isDynamicClass(c) ) // can not wrapper on dynamic class.
c = c.getSuperclass();
//Object类型的
if( c == Object.class )
return OBJECT_WRAPPER;
//先去Wrapper缓存中查找
Wrapper ret = WRAPPER_MAP.get(c);
if( ret == null ) {
//缓存中不存在,生成Wrapper类,放到缓存
ret = makeWrapper(c);
WRAPPER_MAP.put(c,ret);
}
return ret;
}
makeWrapper方法代码不在列出,太长了。就是生成一个继承自Wrapper的类,最后的结果大概是:
public class Wrapper1 extends Wrapper {
public static String[] pns;
public static Map pts;
public static String[] mns; // all method name array.
public static String[] dmns;
public static Class[] mts0;
public String[] getPropertyNames() {
return pns;
}
public boolean hasProperty(String n) {
return pts.containsKey($1);
}
public Class getPropertyType(String n) {
return (Class) pts.get($1);
}
public String[] getMethodNames() {
return mns;
}
public String[] getDeclaredMethodNames() {
return dmns;
}
public void setPropertyValue(Object o, String n, Object v) {
dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl w;
try {
w = ((dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl) $1);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
throw new com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.NoSuchPropertyException("Not found property \"" + $2 + "\" filed or setter method in class dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl.");
}
public Object getPropertyValue(Object o, String n) {
dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl w;
try {
w = ((dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl) $1);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
throw new com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.NoSuchPropertyException("Not found property \"" + $2 + "\" filed or setter method in class dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl.");
}
public Object invokeMethod(Object o, String n, Class[] p, Object[] v) throws java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException {
dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl w;
try {
w = ((dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl) $1);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
try {
if ("sayHello".equals($2) && $3.length == 0) {
w.sayHello();
return null;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException(e);
}
throw new com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.NoSuchMethodException("Not found method \"" + $2 + "\" in class dubbo.provider.hello.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl.");
}
}
生成完Wrapper以后,返回一个AbstractProxyInvoker实例。至此生成Invoker的步骤就完成了。可以看到Invoker执行方法的时候,会调用Wrapper的invokeMethod,这个方法中会有真实的实现类调用真实方法的代码。
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
public JavassistProxyFactory() {
}
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf(36) < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
//返回一个AbstractProxyInvoker,再该invoker调用doInvoke的时候就开始调用:
//具体的包装wrapper中的invokeMethod方法
// if ("sayHello".equals($2) && $3.length == 0) {
// w.sayHello();
// return null;
// }
}
继续
private void exportLocal(URL url) {
if (!"injvm".equalsIgnoreCase(url.getProtocol())) {
URL local = URL.valueOf(url.toFullString()).setProtocol("injvm").setHost("127.0.0.1").setPort(0);
//以上知道proxyFactory.getInvoker(this.ref, this.interfaceClass, local)返回的是AbstractProxyInvoker
Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export(proxyFactory.getInvoker(this.ref, this.interfaceClass, local));
this.exporters.add(exporter);
logger.info("Export dubbo service " + this.interfaceClass.getName() + " to local registry");
}
}
看看protocol.export(bstractProxyInvoker)的执行过程:
//private static final Protocol protocol = (Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
//推测生产出适配类:Protocol$Adaptive,如果有wrapper,则走wrapper,最后会调用dubboProtocol的export
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface Protocol {
int getDefaultPort();
@Adaptive
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> var1) throws RpcException;
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> var1, URL var2) throws RpcException;
void destroy();
}
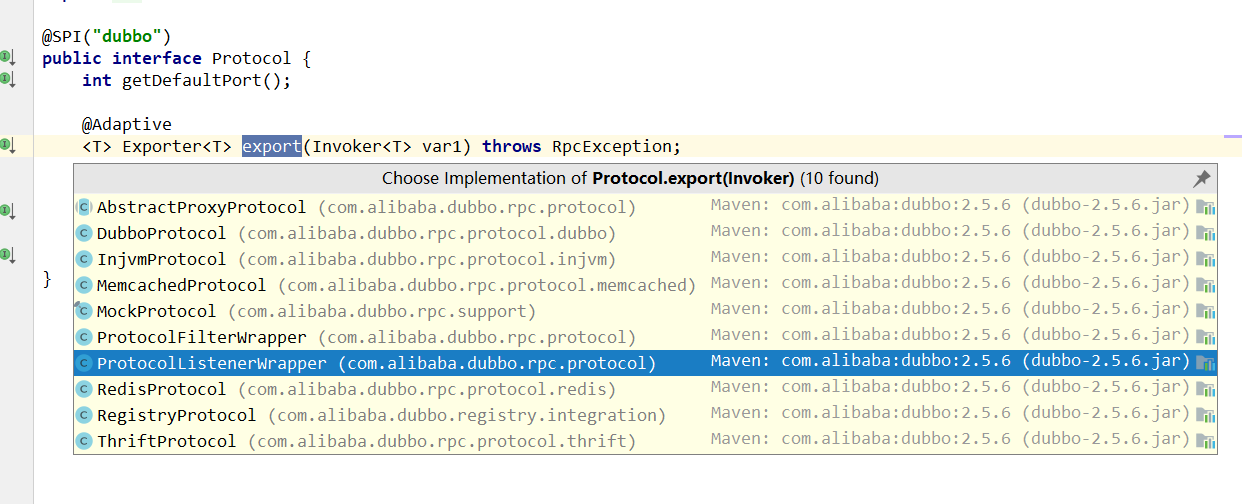
那就是走:
ublic class ProtocolListenerWrapper implements Protocol {
private final Protocol protocol;
public ProtocolListenerWrapper(Protocol protocol) {
if (protocol == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("protocol == null");
} else {
this.protocol = protocol;
}
}
public int getDefaultPort() {
return this.protocol.getDefaultPort();
}
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
return (Exporter)("registry".equals(invoker.getUrl().getProtocol()) ? this.protocol.export(invoker) : new ListenerExporterWrapper(this.protocol.export(invoker), Collections.unmodifiableList(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExporterListener.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), "exporter.listener"))));
}
}
//再走
public class ProtocolListenerWrapper implements Protocol {
private final Protocol protocol;
public ProtocolListenerWrapper(Protocol protocol) {
if (protocol == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("protocol == null");
} else {
this.protocol = protocol;
}
}
public int getDefaultPort() {
return this.protocol.getDefaultPort();
}
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
return (Exporter)("registry".equals(invoker.getUrl().getProtocol()) ? this.protocol.export(invoker) : new ListenerExporterWrapper(this.protocol.export(invoker), Collections.unmodifiableList(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExporterListener.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), "exporter.listener"))));
}
}
最后调用DubboProtocol的export
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
String key = serviceKey(url);
DubboExporter<T> exporter = new DubboExporter(invoker, key, this.exporterMap);//初始化了DubboExporter
this.exporterMap.put(key, exporter);
Boolean isStubSupportEvent = url.getParameter("dubbo.stub.event", false);
Boolean isCallbackservice = url.getParameter("is_callback_service", false);
if (isStubSupportEvent && !isCallbackservice) {
String stubServiceMethods = url.getParameter("dubbo.stub.event.methods");
if (stubServiceMethods != null && stubServiceMethods.length() != 0) {
this.stubServiceMethodsMap.put(url.getServiceKey(), stubServiceMethods);
} else if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("consumer [" + url.getParameter("interface") + "], has set stubproxy support event ,but no stub methods founded."));
}
}
this.openServer(url);
return exporter;
}
查找并初始化话server
private void openServer(URL url) {
String key = url.getAddress();
boolean isServer = url.getParameter("isserver", true);
if (isServer) {
ExchangeServer server = (ExchangeServer)this.serverMap.get(key);//查找serverMap本地缓存有没有ip:20880的server的服务器
if (server == null) {
this.serverMap.put(key, this.createServer(url));
} else {
server.reset(url);
}
}
}
private ExchangeServer createServer(URL url) {
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent("channel.readonly.sent", Boolean.TRUE.toString());
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent("heartbeat", String.valueOf(60000));
String str = url.getParameter("server", "netty");
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported server type: " + str + ", url: " + url);
} else {
url = url.addParameter("codec", Version.isCompatibleVersion() ? "dubbo1compatible" : "dubbo");
ExchangeServer server;
try {
server = Exchangers.bind(url, this.requestHandler);
} catch (RemotingException var5) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to start server(url: " + url + ") " + var5.getMessage(), var5);
}
str = url.getParameter("client");
if (str != null && str.length() > 0) {
Set<String> supportedTypes = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions();
if (!supportedTypes.contains(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str);
}
}
return server;
}
}